Unity3D光照前置知识——Rendering Paths(渲染路径)及LightMode(光照模式)译解
简述
Unity supports different Rendering Paths. You should choose which one you use depending on your game content and target platform / hardware. Different rendering paths have different performance characteristics that mostly affect Lights and Shadows. See render pipeline for technical details.
U3D支持不同的Rendering Path(渲染路径),开发者应该根据游戏内容和目标平台,硬件等来选择使用哪个Rendering Path。不同的Rendering Path具有不同的表现效果,这些不同之处多体现在光照和阴影方面。查阅Render Pipeline获取更多的细节。
The rendering Path used by your project is chosen in Player Settings. Additionally, you can override it for each Camera.
可以在Player Setting中设置默认的Rendering Path,也可以针对单独的Camera进行设置。
If the graphics card can’t handle a selected rendering path, Unity will automatically use a lower fidelity one. For example, on a GPU that can’t handle Deferred Shading, Forward Rendering will be used.
如果目标平台的显卡不能处理所选择的硬件,那么Unity会自动过渡至低保真档次Rendering Path去。比如有的GPU不能处理Deferred Shading,那就会自动采用Forward Rendering。
下面按从高效果至低效果的顺序开始讲解不同的Rendering Path。
Forward Rendering 渲染路径)。同时也不支持Unity3D中的Mesh Renderer组件的Receive Shadows功能,对Culling Masks的支持也不完善,最多能使用四个Culling Mask。
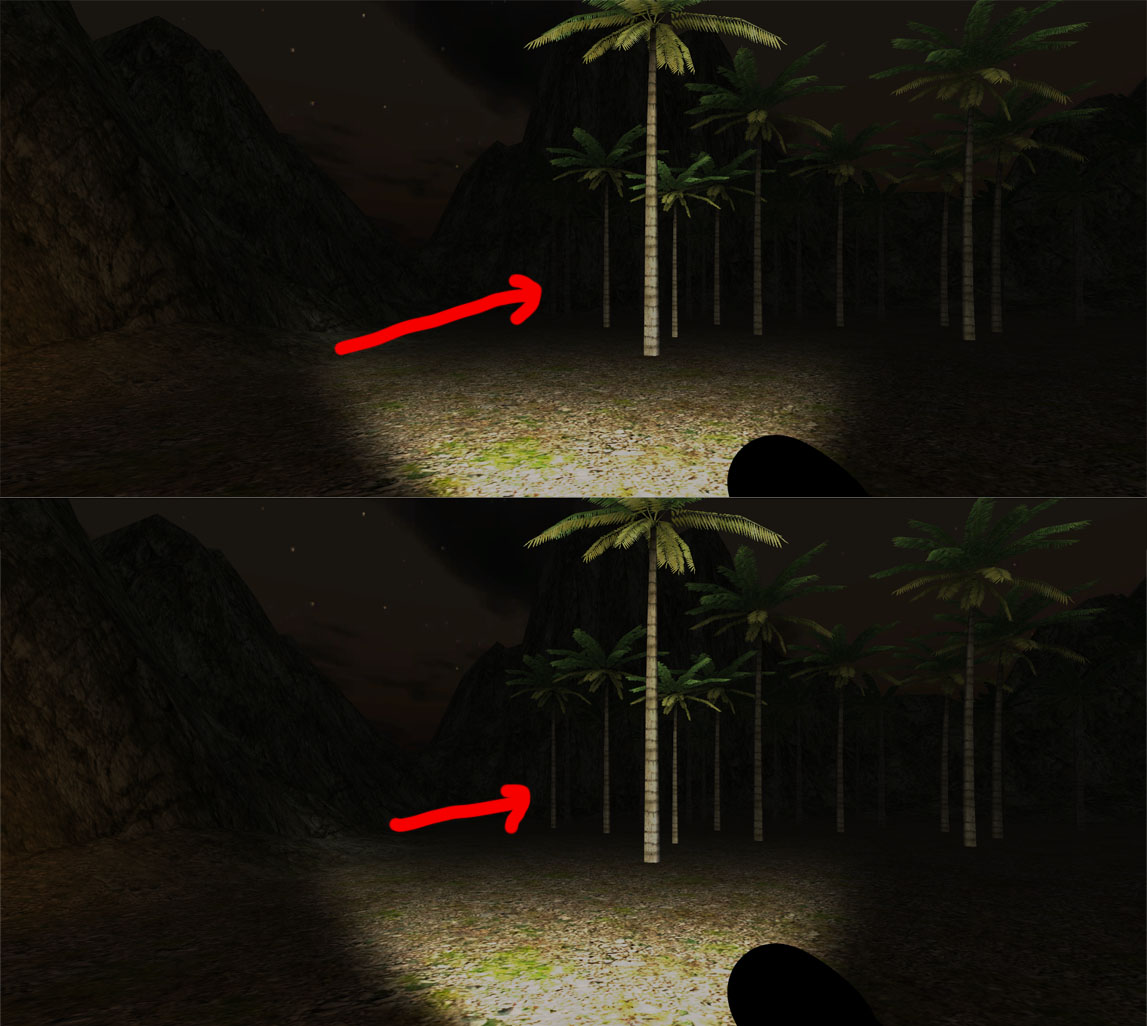
Q: 什么是Light Cookie?
A: Light Cookie又被称作Cucoloris。是一种应用在电影摄制时的小技巧,如下两张图,具体的解释可以查看Wiki,Unity3D中的应用可以查看Unity3D Cookies手册或Unity3d Spot Light Cookie,Unity3D中的实现视频过程可以点击这里:


要求
Q: 什么是Light Cookie?
A: Light Cookie又被称作Cucoloris。是一种应用在电影摄制时的小技巧,如下两张图,具体的解释可以查看Wiki,Unity3D中的应用可以查看Unity3D Cookies手册或Unity3d Spot Light Cookie,Unity3D中的实现视频过程可以点击这里:
显卡应支持Multiple Render Targets(MRT),Shader Model 3.0(及更高),Depth Render Textures。大多数产于2006年以后的PC显卡都支持本功能。
因为对MRT功能支持的缺失,本功能在移动端不受支持。(有的GPU支持,但是支持的程度也非常有限。)
注意:当使用Orthographic projection(正交投影)时Deferred rendering不适用。当使用正交投影时会降至 Forward Rendering。
性能方面
性能方面的影响取决于物体受光源影响的数量,而不是场景的复杂度。小面积的点光源或聚光灯,或光源被部分或完全摭挡,可以在很好的降低性能开销。
有阴影的光源开销更大,在Deferred rendering中,受到投影光源影响的,且可投影的物体依然是要对影响其的每个投影光源都进行计算。具有阴影的光照Shader也肯定比没有阴影的开销更大。
点击这里 ,提问者最后通过调整光照亮度得以解决。
Light Popping现象
Base Pass
Base Pass只用一个per-pixel光源和所有的SH/Vertex 光源来渲染物体。在这个pass内也能通过shader加入光照贴图(Lightmaps),环境光(ambient),自发光(Emissive)等。平行光在这个Pass内产生阴影。
注意:
- 使用LightMaps的物体(烘培过的物体)不会受到SH光源的光照。
- 当在Shader中使用Passflag tag “OnlyDirectional”时,forward base pass只会渲染主平行光,环境光照探头(Ambient/Light Probe)和光照贴图,SH和vertex光源没有被包含在此pass的数据内。
Additional Passes
Additional Passes用于渲染每个额外的per-pixel光源。在这些pass中的光源默认是不会产生阴影的(也就是说,Forward Rendering默认只支持一个光源可以产生阴影)。除非使用multi_compile_fwdadd_fullshadows宏。
性能相关
Spherical Harmonics lights(球谐光照)非常高效。对CPU的消耗极其微小,对于GPU来说不会有额外的负担(因为base pass原本就会一直计算SH Lighting;和球谐光照的机制有光,无论有多少球谐光的存在,消耗都是一样的)。
扩展阅读,Enlighten的简化球谐光照文档,《球谐照明:细节》,《球谐照明:细节》讲义,球谐照明原理
SH光照的缺点:
- 利用物体的vertices(Vertex单词的复数形式,Vertex的复数有三种写法: vertexes,vertices ,vertexs)进行计算,而不是pixels。因此不支持法线贴图和Light Cookies。
- SH光照函数是种非常低频的照明函数,不会有非常锐利的照明过渡,另外也只会响应Diffuse Lighting(漫反射),对于Specular Highlight(镜面高光)而言其频率太低了。
- SH lighting is not local; point or spot SH lights close to some surface will “look wrong”. 球谐照明不是局部的(?局部坐标系?),点光源或聚光灯形式的SH Light在靠近一些表面时看上去会不正常。
总结,SH Light适用于小型动态物体。
RTR(Real-Time Rendering)网站的文章《Deferred lighting approaches》
Deferred Lighting从Unity 5.0起被视为传统特性,因为其无法支持诸如Stander Shader,Reflection Probes等特性。新工程可以考虑直接使用 Deferred Shading(不适用于移动平台)。
注意:当使用Orthographic projection时Deferred Rendering Path 不适用。当使用正交投影时会降至 Forward Rendering Path。
注意:Legacy Deferred Lighting Rendering Path 和 Deferred Shading Rendering Path 都是Deferred rendering。
Deferred Lighting对影响物体的光源数量没有限制,所有的光源都是Per-Pixel光照,即所有光源都可以正确的和法线贴图得到正确的计算结果。另外,所有的光源都可以有Light Cookie和Shadow。其性能开销与光源数量成正比,这意味着可以通过控制光照面积,减少单个物体受到光照影响的数量来获得性能方面的提升。Deferred Lighting的另一个优点是结果能够很方便的预测,被个光源都是逐像素光照,具有一致的光照计算过程。
其缺点在于不能真正的支持抗锯齿以及半透明物体(半透明物体采用 Forward Rendering 渲染路径)。同时也不支持Unity3D中的Mesh Renderer组件的Receive Shadows功能,对Culling Masks的支持也不完善,最多能使用四个Culling Mask。
要求
显卡应支持Shader Model 3.0(或更新的版本),Depth Render Textures,Two-sided Stencil Buffers。大多数产于2004年以后的PC显卡都支持本功能。
在手机端,所有支持OpenGL ES 3.0r GPU都支持Deferred Lighting. 部份OpenGL ES 2.0的GPU也能支持(因为支持Depth Textures)。
注意:当使用Orthographic projection(正交投影)时Deferred rendering不适用。当使用正交投影时会降至 Forward Rendering。
性能方面
性能方面的影响取决于物体受光源影响的数量,而不是场景的复杂度。小面积的点光源或聚光灯,或光源被部分或完全摭挡,可以在很好的降低性能开销。
有阴影的光源开销更大,在Deferred Rendering中,受到投影光源影响的,且可投影的物体依然是要对影响其的每个投影光源都进行计算。具有阴影的光照Shader也肯定比没有阴影的开销更大。
使用指南
使用Deferred Lighting, 渲染过程发生在三种Pass内。
- Base Pass:物体产生screen-space buffers, 包含depth, normals, specular power等信息。
- Lighting Pass:前一阶段生成的Scree-space buffers用来计算光照,并放入另一个screen-space buffers。
- Final Pass:物体再次被处理,取得前一阶段计算的光照信息,结合色彩纹理,并添加ambient/emissive Lighting。
如果物体使用了不适用于Deferred Lighting Rendering Path的Shader,会使用Forward rendering path
Base Pass
Base pass会对物体进行一次处理。View sapce normals(视野空间法线)和Specular Power(高光强度)被处理为一张ARGB32格式的Shader Replacement的Shader中进行处理。
Lighting Pass
lighting passs根据Depth,Normal和Specular power来计算光照。光照计算发生在Screen Space(屏幕空间)中,因此时间消耗取决与场景的复杂程度。Lighting Buffer是一张ARGB32的Render Texture,Diffuse Lighting使用其RGB通道,Specular Lighting使用其A通道。
Final Pass
处理纹理,自发光等其它内容,另外,光照贴图也在这里完成。
Legacy Vertex Lit Rendering Path
Shader中使用的 使用的LightMode Pass Tag: Vertex,VertexLMRGBM和VertexLM
效果最差,不支持实时阴影。属于Forward Rendering Path的子集。是性能最高,受支持度最多的Rendering Path(但是主机上不适用)。
所有的光照计算在Vertex层面完成,因此无法支持大多数的per-pixel效果,比如,阴影,法线贴图,Light Cookies,精细的高光效果。
LightMode Tags
LightMode tag defines Pass’ role in the lighting pipeline. See render pipeline for details. These tags are rarely used manually; most often shaders that need to interact with lighting are written as Surface Shaders and then all those details are taken care of.
Possible values for LightMode tag are:
Always: Always rendered; no lighting is applied.
ForwardBase: Used in Forward rendering, ambient, main directional light, vertex/SH lights and lightmaps are applied.
ForwardAdd: Used in Forward rendering; additive per-pixel lights are applied, one pass per light.
Deferred: Used in Deferred Shading; renders g-buffer.
ShadowCaster: Renders object depth into the shadowmap or a depth texture.
PrepassBase: Used in legacy Deferred Lighting, renders normals and specular exponent.
PrepassFinal: Used in legacy Deferred Lighting, renders final color by combining textures, lighting and emission.
Vertex: Used in legacy Vertex Lit rendering when object is not lightmapped; all vertex lights are applied.
VertexLMRGBM: Used in legacy Vertex Lit rendering when object is lightmapped; on platforms where lightmap is RGBM encoded (PC & console).
VertexLM: Used in legacy Vertex Lit rendering when object is lightmapped; on platforms where lightmap is double-LDR encoded (mobile platforms).
Rendering Paths Comparison
| - | Deferred | Forward | Legacy Deferred | Vertex Lit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Features | ||||
| Per-pixel lighting (normal maps, light cookies) | Yes | Yes | Yes | - |
| Realtime shadows | Yes | With caveats | Yes | - |
| Reflection Probes | Yes | Yes | - | - |
| Depth&Normals Buffers | Yes | Additional render passes | Yes | - |
| Soft Particles | Yes | - | Yes | - |
| Semitransparent objects | - | Yes | - | Yes |
| Anti-Aliasing | - | Yes | - | Yes |
| Light Culling Masks | Limited | Yes | Limited | Yes |
| Lighting Fidelity | All per-pixel | Some per-pixel | All per-pixel | All per-vertex |
| Performance | ||||
| Cost of a per-pixel Light | Number of pixels it illuminates | Number of pixels * Number of objects it illuminates | Number of pixels it illuminates | - |
| Number of times objects are normally rendered | 1 | Number of per-pixel lights | 2 | 1 |
| Overhead for simple scenes | High | None | Medium | None |
| Platform Support | ||||
| PC (Windows/Mac) | Shader Model 3.0+ & MRT | All | Shader Model 3.0+ | All |
| Mobile (iOS/Android) | OpenGL ES 3.0 & MRT | All | OpenGL ES 2.0 | All |
| Consoles | XB1, PS4 | All | XB1, PS4, 360 | - |